腫瘤的重點有五個
1.腫瘤的分類和標記
2.腫瘤形成(環境致癌、化學致癌、放射線致癌、微生物致癌)
3.腫瘤與基因、遺傳
4.腫瘤分子病理(致癌、抑癌、其他輔助基因等)
5.腫瘤動力(侵犯、血管生成、轉移)及副腫瘤症候群 (腫瘤伴隨症候群)
分子病理分類
- 分為genetic和epigenetic兩種
- Genetic基因的成因
- 研究直接或高度相關導致癌症的基因
- 主要有四大類
- Oncogene
- Tumor suppressor gene
- Apoptotic gene
- DNA repair gene
- Epigenetic基因上的成因
- 又稱為表觀遺傳學
- 主要為研究基因的表現和修飾,了解這些機制如何在不影響基因序列的情況下,達到調控基因表現,進而影響生物的表現型(phenotype)
- 主要有三大類
- Histone modification
- DNA methylation
- Non-coding RNA
- 腫瘤初始常為homogenous and monoclonal,但隨著時間的推進,會逐漸變為heterogenous
- The hallmarks of cancer and possible target
- Sustaining proliferative signaling ← Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors
- Evading growth suppressors ← Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
- Avoiding immune destruction ← Immune activating anti-CTLA4 monoclonal antibody
- Enabling replicative immortality ← Telomerase inhibitors
- Tumor-promoting inflammation ← Selective anti-inflammatory drugs
- Activating invasion & metastasis ← Inhibitors of HGF/c-Met
※ Hepatocyte growth factor, HGF - Inducing angiogenesis ← Inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling
- Genome instability & mutation ← poly ADP- ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors
- Resisting cell death ← Proapoptotic BH3 mimetics
- Deregulating cellular energetics ← Aerobic glycolysis inhibitors
導致癌症的基因(genetic)
- Oncogene致癌基因(啟動)
- 常和這五大類有關
- Growth factors
- Growth factor receptors
- Signal transduction proteins
- Transcription activators
- Cell cycle regulators
- 主要的細胞週期相關分子及其抑制
- Cyclin-dependent kinases
CKD4:Forms a complex with cyclin D that phosphorylates RB, allowing the cell to progress through the G1 restriction point
CDK2:Forms a complex with cyclin E in late G1, which is involved in G1/S transition. Forms a complex with cyclin A at the S phase that facilitates G2/M transition
CDK1:Forms a complex with cyclin B that facilitates G2/M transition - Inhibitors
CIP/KIP family:p21, p27 (CDKN2A-C):Block the cell cycle by binding to cyclin-CDK complex; p21 is induced by the tumor suppressor p53; p27 responds to growth suppressors such as TGF-β
INK4/ARF family (CDKN1A-D):p16/INK4a binds to cyclin D-CDK4 and promotes the inhibitory effects of RB; p14/ARF increases p53 levels by inhibiting MDM2 activity - Checkpoint components
p53:Tumor suppressor gene altered in the majority of cancer, causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Acts mainly through p 21 to cause cell cycle arrest. Causes apoptosis by inducing the transcription of pro-apoptotic genes such as BAX. Levels of p53 are negatively regulated by MDM2 through a feedback loop. p53 is required for the G1/S checkpoint and is a main component of the G2/M checkpoint
Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated:Activated by mechanisms that sense double-stranded DNA breaks. Transmits signals to arrest the cell cycle after DNA damage. Acts through p53 in the G1/S checkpoint. At the G2/M checkpoint, it acts both through p53-dependent mechanisms and through the inactivation of CDC25 phosphatase, which disrupts the cyclin B-CDK1 complex. Component of a network of genes that include BRCA1 and BRCA2, which link DNA damage with cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
- Cyclin-dependent kinases
- 其他重要舉例
- Erythroblastic oncogene B = ERBB2 = Her-2 = human epidermal-growth-factor receptor 2,EGFR家族,此基因的放大(amplification)會導致乳癌或卵巢癌
- Rearranged during transfection gene = RET基因,是一種colony stimulating factor receptor -1 (CSF-1R),點突變造成MEN第二型、medullary thyroid carcinoma,rearrangement則造成papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Retrovirus-associated DNA sequences = Ras,為最常見的致癌基因,為GTP-binding protein,常見於胰臟癌、肺癌、結腸癌等
- Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 = ABL1或簡稱為ABL,此基因決定了一種tyrosine kinase,轉位(translocation)並與BCR融合(fusion)後,為費城染色體(Philadelphia chromosome),造成chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
- Cellular myelocytomatosis = c-Myc,產物為轉錄因子,其轉位(translocation)與Burkitt lymphoma有關;N-Myc,N可能為nucleus或neuroblastoma…(待查證),可以均質染色區(homogenous staining region, HSR)或雙微體(double minutes)的方式放大(amplification),此基因的放大容易導致neuroblastoma
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 = CDK4,調控細胞週期,melanoma常是此基因發生點突變或放大造成
- 常和這五大類有關
- Tumor suppressor gene抑癌基因(缺失、未作用)
- Selected tumor suppressor genes involved in human neoplasms
- 共可以分為cell surface、inner aspect of plasma membrane、cytoskeleton、cytosol、nucleus這幾大類
- 細節可以參考http://teachingcenter1.pixnet.net/blog/post/354439919
- NF-1可以抑制Ras,若NF-1缺失會造成neurofibromatosis type 1
- APC可以分解轉譯分子前驅物β-catenin,為家族性大腸息肉症的守門基因
- 最重要的抑癌基因為p53基因,位於17p13.1,可活化p21使G1 phase停下,活化GADD45進行修復,若不行則活化bax造成細胞死亡,大多癌症多有p53基因的缺失或突變,而Li-Fraumeni syndrome為先天p53缺乏,病患容易同時產生多種癌症
- Rb為細胞週期調節基因,缺失時會造成retinoblastoma (60%偶發、40%家族性)及osteosarcoma,另外Rb基因所產生的蛋白,還有促進細胞分化及induce senescence的功能(pocket protein-E2F network)
- BRCA1和BRCA2會參與DNA修復,缺失時與乳癌有關
- 二次打擊假說(two-hit hypothesis)
- 抑癌基因兩個allele都缺失才會致癌,故需要兩次打擊
- 第一次大多為點突變(遺傳),第二次多為刪除(deletion,後天)
- 故出生時為heterozygous,第二次打擊後變成homozygous mutation,稱為loss of heterozygosity (LOH)
- p16INK4a/cyclin D/CKD4/Rb為四個關鍵的細胞週期調控,大部分癌症多有任一個以上的缺失
- Selected tumor suppressor genes involved in human neoplasms
- Apoptotic gene凋亡基因(未啟動(?))
- 一般來說,癌症細胞被認為是抑制了自身的凋亡,所以得以不斷的分裂、增大,例如最著名的bcl-2基因,會抑制細胞凋亡,他的過度活化,會造成follicular lymphoma
- 但也有另一派的假說,認為正常細胞的凋亡,可能會釋放出誘使周遭細胞癌化的分子,認為細胞的凋亡有可能反而是誘發癌症發生的原兇(之一?),此假說目前討論的不多,比較詳細的解釋發表在2016年的《Nature Reviews Cancer》A fate worse than death: apoptosis as an oncogenic process
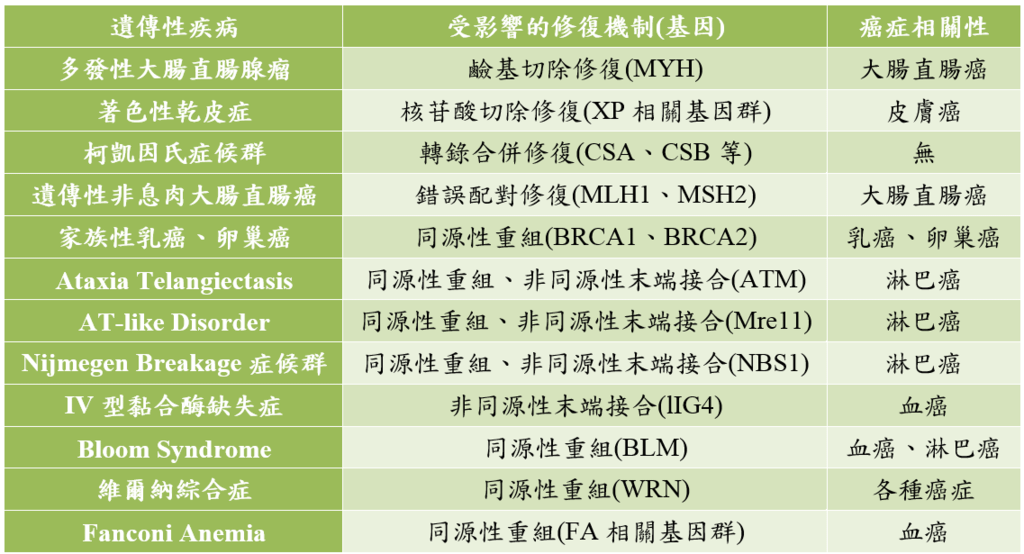
- DNA repair gene修復DNA的基因(被破壞)
|
受影響的修復機制(基因) |
癌症相關性 |
|
|
多發性大腸直腸腺瘤 |
鹼基切除修復(MYH) |
|
|
核苷酸切除修復(XP相關基因群) |
||
|
轉錄合併修復(CSA、CSB等) |
無 |
|
|
遺傳性非息肉大腸直腸癌 |
錯誤配對修復(MLH1、MSH2) |
|
|
家族性乳癌、卵巢癌 |
同源性重組(BRCA1、BRCA2) |
|
|
Ataxia Telangiectasis |
同源性重組、非同源性末端接合(ATM) |
|
|
AT-like Disorder |
同源性重組、非同源性末端接合(Mre11) |
淋巴癌 |
|
Nijmegen Breakage症候群 |
同源性重組、非同源性末端接合(NBS1) |
淋巴癌 |
|
非同源性末端接合(lIG4) |
||
|
Bloom Syndrome |
同源性重組(BLM) |
血癌、淋巴癌 |
|
同源性重組(WRN) |
各種癌症 |
|
|
Fanconi Anemia |
同源性重組(FA相關基因群) |
血癌 |
- 重要的守門基因:Rb、NF-1、VHL(3p)、APC
重要的translocation:t(8;14)(myc, Burkitt lymphoma)、t(9;22)(費城染色體造成CML)、t(8;14)(bcl-2活化造成follicular lymphoma)、t(15;17)(retinoid acid receptor, AML)、t(11;14)(cyclin D1, mantle cell lymphoma)
導致癌症的基因表現或修飾(epigenetic)
- Histone modification (組蛋白修飾)
- 包含乙醯化(acetylation)、磷酸化(phosphorylation)、甲基化(methylation)以及泛素化(ubiquitination)
- 組蛋白不同位置的胺基酸如果被甲基化,可能正向或負向調控基因的表現
- 而當啟動子區域的組蛋白被乙醯化時,會促進基因的轉錄
- 乙醯基團轉移至組蛋白的lysine residues時,會導致染色質的結構打開,進而促進基因轉錄
- 而將乙醯基團移除,則會抑制此基因的表現
- 目前認為histone modification與DNA的轉錄、修復、重組、複製相關
- DNA methylation (DNA甲基化)
- 此過程參與許多調控,包含chromosome stability、chromatin structure、X chromosome inactivation、embryonic development、transcription等
- CpG islands在活化的基因中與轉錄、啟始部位、啟動子有關,細胞可以藉由對此部位甲基化來調控基因表現
- Non-coding RNA (非編碼核醣核酸)
- 包含micro RNA、small RNA、large RNA、pi-RNA等
- 這些非編碼核醣核酸也會影響到基因的轉錄與轉譯



 留言列表
留言列表